In 1988, I learned to ride a skateboard. There was no PowerPoint presentation involved, no lectures, and no eLearning modules. I just got on and had a go! I didn’t stay on for more than 5 seconds before falling off, but it was after the board shot out from underneath me that I had time to re-wire my mind and adapt my strategy for the next go based on what I’d experienced during those 5 seconds. That’s experiential learning!
The second time around, 15 seconds on the board, and the same process again repeatedly until I had, within a few hours, achieved a level of competency that meant that although I wasn’t necessarily ready to skateboard at the Olympics, I had learned how to ride a skateboard well enough, simply by the power of learning by doing!
In today’s rapidly changing world, traditional classroom-based learning alone, whilst there is a place for it, may not be enough in isolation to prepare students and professionals for the challenges they will face in the workplace. Enter experiential learning, a dynamic approach that bridges the gap between theory and practice, enriching the educational experience and fostering a deeper understanding of subjects.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) reported in 2020 that “40% of current workers’ core skills are expected to change in the next 5 years”, with 50% of all employees needing to be reskilled by 2025. Higher education will play a vital role in addressing this evolution.
What is Experiential Learning?
Built on the relatively simple yet eminently powerful concept that the only way to get people to believe in an idea is to get them to believe it was their own idea in the first place, ‘experiential learning’ is an educational philosophy that emphasizes learning through direct, hands-on experiences. It goes beyond simply repetitive memorization and passive absorption of knowledge, encouraging learners to actively engage with the material. This approach is built on the idea that people learn best by doing, reflecting, and applying their knowledge in real-world situations.
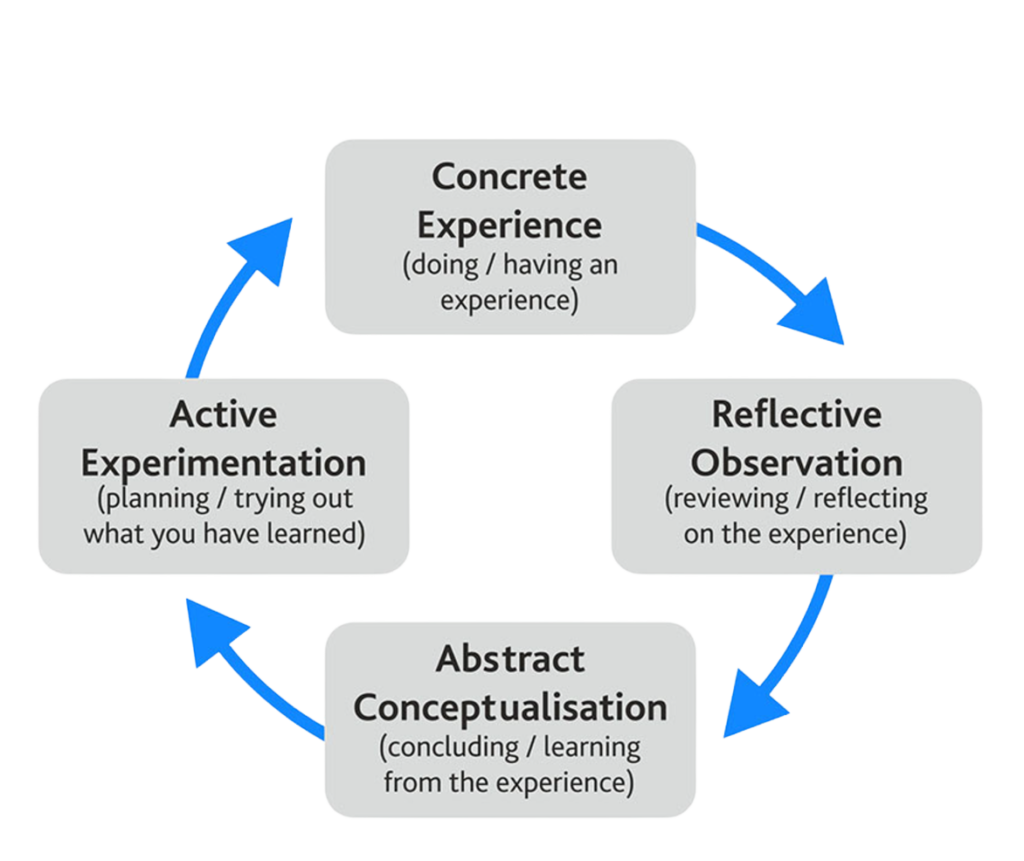
In the 1980s, David Kolb (Harvard University) wrote down the experiential learning cycle we see here.
David Kolb’s Experiential Learning Cycle
It starts very simply with a concrete experience, so in my case just getting on the skateboard and having a go. I then undertook a period of reflective observation to consider how the experience made me feel. Was it positive? Negative? This led to the abstract conceptualization whereby I’m making conclusions about the experience and thinking “When I get back on the board, what’s my strategy this time? What do I want to do differently to have more success?”
I then move into active experimentation to put directly into practice my new and revised approach and strategy for being more competent on the second attempt, which as the attempts increase, becomes more and more fruitful each time throughout this process.
What Problems does Experiential Learning Address?
Whilst there is always a valuable place for traditional learning methods, it is also fair to say based on fairly extensive research, that there are some well-evidenced problems with those traditional methods, such as:
* Lack of engagement
* Workforce resistance
* Not always relevant: often in this world of increased individualized learning and development it’s focused on the individual, not the group, so contextualizing learning and putting it into practice effectively on the ground can be problematic.
* Lacks contextual feedback
* Information overload: often way too much information for individuals to be able to take complex concepts on board and apply them in real-world settings.
In fact, the research into these dates back to 1885, with Herman Ebbinghaus. Ebbinghaus’s study focused on voluntary and involuntary memory, revealing that if you are learning something in a traditional way on day zero, within 30 days you’re down to about 20% retention unless you’ve gone back and revisited it several times, in which case you can get the retention up to about 80%. Many people of course do not have the time to revisit those learnings to be able to achieve this, and that in itself renders many traditional learning methods at a disadvantage from an efficacy perspective.
How does Experiential Learning add value?
1. Active Engagement: Experiential learning promotes active involvement, challenging participants to take on tasks, make decisions, and solve problems, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
2. Reflection: After any hands-on experience, learners reflect on what they’ve encountered and learned. This self-assessment deepens understanding and connects theory to practice.
3. Application: Experiential learning emphasizes the active application of acquired knowledge and skills in real-life situations. This encourages the development of practical skills that are immediately relevant.
4. Feedback: Constructive feedback is integral to the process. Learners receive guidance on their performance, which helps them improve and refine their abilities.
5. Increased Retention: Learners retain information for longer and understand concepts more deeply when they actively engage with the material.
6. Real-World Relevance: Individuals are prepared for the complexities and challenges of the real world, bridging the gap between academia and practical workplace application.
7. Personal Growth: Participants experience personal growth and increased self-confidence as they overcome challenges and learn from their experiences.
8. Preparation for the Future: Experiential learning equips individuals with skills and knowledge they can immediately apply in their careers, fostering adaptability and readiness for an ever-changing world.
Experiential Learning in the Higher Education Setting
1. Supporting Student Employability: Simulation-based learning is a valuable way to provide students with the opportunity to experience the running of a business (for example) in a safe space. Learning to fail fast and making iterative improvements to develop an agile methodology for running a successful organization is a valuable addition to employability initiatives across higher education.
2. Soft Skills Development: Communication, teamwork, inclusivity, adaptability, time management, leadership, conflict management, problem solving, persuasion, and openness to criticism. These are all vital skills that experiential learning can surface and actively be worked on in real-time as students apply themselves to specific challenges.
3. ‘Oven-Ready’ Graduates: As the world of work continues to evolve at pace with the ever-emerging opportunities created by AI for example, cross-modular learning in subjects such as Business is creating greater flexibility which can be further explored through interdisciplinary experiential learning to produce graduates ‘oven-ready’ for the world of work in 2023 and the future.
4. Project-Based Learning: Learners work on authentic, long-term projects that require collaboration, problem-solving, and the application of subject matter knowledge.
5. Sustainable Thinking: In support of increasing ESG thinking in organizations worldwide, the role higher education can play in introducing students to this thinking through the power of simulation-based activities is an important one, not to be underestimated.